 Pages 34-40
Pages 34-40by Kamil Ibrahimov
Baku´s Old City is a treasure trove of Azerbaijani history. Its stone buildings and mazy streets hold secrets that have still to be discovered. A masterpiece of Old City architecture, rich in history but with questions still unanswered, is the medieval residence of the rulers of Shirvan, the Shirvanshahs´ Palace.
The State of Shirvan
The state of Shirvan was formed in 861 and became the longest-surviving state in northern Azerbaijan. The first dynasty of the state of Shirvan was the Mazyadi dynasty (861-1027), founded by Mahammad ibn Yezid, an Arab vicegerent who lived in Shamakhi.
In the 10th century, the Shirvanshahs took Derbent, now in the Russian Federation. Under the Mazyadis, the state of the Shirvanshahs stretched from Derbent to the Kur River. The capital of this state was the town of Shamakhi.
In the first half of the 11th century, the Mazyadi dynasty was replaced by the Kasrani dynasty (1028-1382). The state of Shirvan flourished under the Shirvanshahs, Manuchehr III and his son Akhsitan. The last ruler in this dynasty was Hushang. His reign was unpopular and Hushang was killed in a rebellion.
The Kasrani dynasty was later replaced by the Derbendi dynasty (1382-1538), founded by Ibrahim I (1382-1417). Ibrahim I was a well-known but bankrupt feudal ruler from Shaki. His ancestors had been rulers in Derbent, hence the dynasty´s name. Ibrahim was a wise and peace-loving ruler and for some time managed to protect Shirvan from invasion.
To prevent the country´s destruction by Timur (Tamerlane), Ibrahim I took gifts to Timur´s headquarters and obtained internal independence for Shirvan. Ibrahim I failed to unite all Azerbaijani lands under his rule, but he did manage to make Shirvan a strong and independent state.
Baku becomes capital of Shirvan
The 15th century was a period of economic and cultural revival for Shirvan. Since this was a time of peace in Shirvan, major progress was made in the arts, architecture and trade. Shamakhi remained the capital of Shirvan at the start of the century, but an earthquake and constant attacks by the Kipchaks, a Turkic people, led the capital to be moved to Baku.
The city of Baku was the capital of the country during the rule of the Shirvanshahs Khalilullah I (1417-62) and his son Farrukh Yasar (1462-1500).
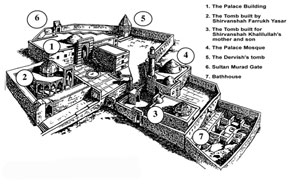
While tension continued in Shamakhi, Baku developed in a relatively quiet environment. It is known that strong fortress walls were built in Baku as early as the 12th century. After the capital was moved to Baku, the Palace of the Shirvanshahs was erected at the highest point of the city, in what had been one of the most densely populated areas. The palace complex consists of nine buildings - the palace itself, the Courtroom, the Dervish´s Tomb, the Eastern Gate, the Shah Mosque, the Keygubad Mosque, the palace tomb, the bathhouse and the reservoir.
The buildings of the complex are located in three courtyards that are on different levels, 5.6 metres above one another. Since the palace is built on uneven ground, it does not have an orderly architectural plan. The entire complex is constructed from limestone. Of all the buildings, the palace itself has suffered the most wear and tear over the years. The palace was looted in 1500 after Farrukh Yasar was killed in fighting between the Shirvanshahs and the Safavids. As the Iranian and Ottoman empires vied for power in the South Caucasus, the state of Shirvan, on the crossing-point of various caravan routes, suffered frequent attacks. Consequently, the palace was badly damaged many times. Proof of this is the Murad Gate which was built during Ottoman rule.
What is now Azerbaijan was occupied by Russia on 10 February 1828. The Shirvanshahs´ Palace became the Russian military headquarters and many palace buildings were destroyed. In 1954, the Complex of the Palace of the Shirvanshahs was made a State Historic-Architectural Reserve and Museum. In 1960, the authorities of the Soviet republic decided to promote the palace as an architectural monument.
The Palace Building
The palace is a two-storey building in an irregular, rectangular shape. In order to provide better illumination of the palace, the south-eastern part of the building was constructed on different levels. Initially there were 52 rooms in the palace, of which 27 were on the ground floor and 25 on the first floor. The shah and his family lived on the upper floor, while servants and others lived on the lower floor.
The Tomb Built by Shirvanshah Farrukh Yasar (also known as the Courtroom or Divankhana)
Shirvanshah Farrukh Yasar had the tomb constructed in the upper courtyard of the palace complex. Its north side and one of its corners adjoin the residential building. The tomb consists of an octagonal rotunda, completed with a dodecagonal dome. Its octagonal hall is surrounded by an open balcony or portico. The balcony is edged with nine columns which still have their original capitals. The rotunda stands in a small courtyard which also has an open balcony running around its edge. The balcony´s columns and arches are the same shape as those of the rotunda. The outer side of the columns has a stone with the image of a dove, the symbol of freedom, and two stone chutes to drain water away. Some researchers believe that this building was used for official receptions and trials and call it the Courtroom. The architectural work in the tomb was not completed.
The tomb is considered one of the finest examples of medieval architecture, not only in Azerbaijan but in the whole Middle East.
The Dervish´s Tomb
The Dervish´s Tomb is located in the southern part of the middle courtyard. Some historians maintain that it is the tomb of Seyid Yahya Bakuvi, who was a royal scholar and astronomer under Khalilullah I. Other historians say that all the buildings in the lower courtyard of the palace, including the Dervish´s Tomb, are part of a complex where dervishes lived, but there is little evidence for this.
The Keygubad Mosque
Now in ruins, the Keygubad Mosque was a mosque-cum-madrasah joined to the Dervish´s Tomb. The tomb was located in the southern part of the mosque. The mosque consisted of a rectangular prayer hall and a small corridor in front of it. In the centre of the hall four columns supported the dome. Historian Abbasgulu Bakikhanov wrote that Bakuvi taught and prayed in the mosque: "The cell where he prayed, the school where he worked and his grave are there, in the mosque". Keygubad Shirvanshah ruled from 1317 to 1343 and was Sheikh Ibrahim´s grandfather.
The Eastern Gate
The Eastern or Murad Gate is the only part of the complex that dates to the 16th century. Two medallions on the upper frame of the Murad Gate bear the inscription: "This building was constructed under the great and just Sultan Murad III on the basis of an order by Racab Bakuvi in 994" (1585-86).
The Tomb of the Shirvanshahs
There are two buildings in the lower courtyard - the tomb and the Shah Mosque. A round wall encloses the lower courtyard, separating it from the other yards. When you look at the tomb from above, you can see that it is rectangular in shape, decorated with an engraved star and completed with an octagonal dome. While the tomb was being built, blue glazed tiles were placed in the star-shaped mortises on the dome.
An inscription at the entrance says: "Protector of the religion, man of the prophet, the great Sultan Shirvanshah Khalilullah, may God make his reign as shah permanent, ordered the building of this light tomb for his mother and seven-year-old son (may they rest in peace) 839" (1435-36). The architect´s name is also inscribed between the words "God" and "Mohammad" on another decorative inscription on the portal which can be read only using a mirror. The inscription says "God, architect Ali, Mohammad".
A skeleton 2.1 metres tall was found opposite the entrance to the tomb. This is believed to be Khalilullah I´s own grave. A comb, a gold earring and other items of archaeological interest were found there.
The Shah Mosque
The Shah Mosque is in the lower courtyard, alongside the mausoleum. The mosque is 22 metres high. An inscription around the minaret says: "The Great Sultan Khalilullah I ordered the erection of this minaret. May God prolong his rule as Shah. Year 845" (1441-42).
Stairs lead from a hollow in the wall behind the minbar or pulpit to another small room. Stone traceries on the windows decorate the mosque.
The Palace Bathhouse
The palace bathhouse is located in the lowest courtyard of the complex. Like all bathhouses in the Old City, this one was built underground to ensure that the temperature inside was kept stable. As time passed the level of the earth rose and covered it completely. The bathhouse was found by chance in 1939. In 1953 part of it was cleaned and in 1961 restoration work was done and the dome repaired. The walls in one of the side rooms are covered with glazed tiles and this room is thought to have been the shah´s room.
Cistern
The cistern, part of an underground water distribution system, was constructed in the lower part of the bathhouse to supply the Shirvanshahs´ Palace with water. Water came into the cistern via ceramic pipes which were part of the Shah´s Water Pipeline, laid from a high part of the city. The cistern is located underground and its entrance has the shape of a portal. Numerous stairs lead from the entrance down to the storage facility. A link between the cistern and the bathhouse can be seen from the side lobby. The cistern was found by chance during restoration work in 1954.Literature
S.B. Ashurbayli: Государство Ширваншахов (The State of the Shirvanshahs), Baku, Elm, 1983; and Bakı şəhərinin tarixi (The History of the City of Baku), Baku, Azarnashr, 1998.
F.A. Ibrahimov and K.F. Ibrahimov: Bakı İçərişəhər (Baku Inner City), Baku, OKA, Ofset, 2002. Kamil Farhadoghlu: Bakı İçərişəhər (Baku Inner City), Sh-Q, 2006; and Baku´s Secrets are Revealed (Bakının sirləri açılır), Baku, 2008.
E.A. Pakhomov: Отчет о работах по шахскому дворцу в Баку (Report on Work in the Shah´s Palace in Baku), News of the AAK, Issue II, Baku, 1926;
and Первоначальная очистка шахского дворца в Баку (Initial Clearing of the Shah´s Palace in Baku), News of the AAK, Issue II, Baku, 1926.
Chingiz Gajar: Старый Баку (Old Baku), OKA, Ofset, 2007.
M. Huseynov, L. Bretanitsky, A. Salamzadeh, История архитектуры Азербайджана (History of the Architecture of Azerbaijan). Moscow, 1963.
M.S. Neymat, Корпус эпиграфических памятников Азербайджана (Azerbaijan´s Epigraphic Monuments), Baku, Elm, 1991.
A.A. Alasgarzadah, Надписи архитектурных памятников Азербайджана эпохи Низами (Inscriptions on the architectural monuments of Azerbaijan from the era of Nizami) in the collection, Архитектура Азербайджана эпохи Низами (Azerbaijan in the Era of Nizami), Moscow, 1947.








.jpg)